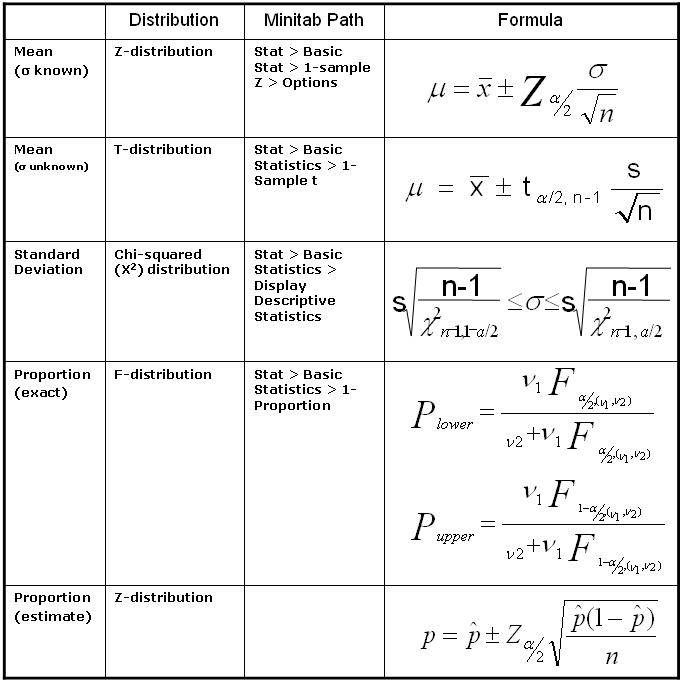
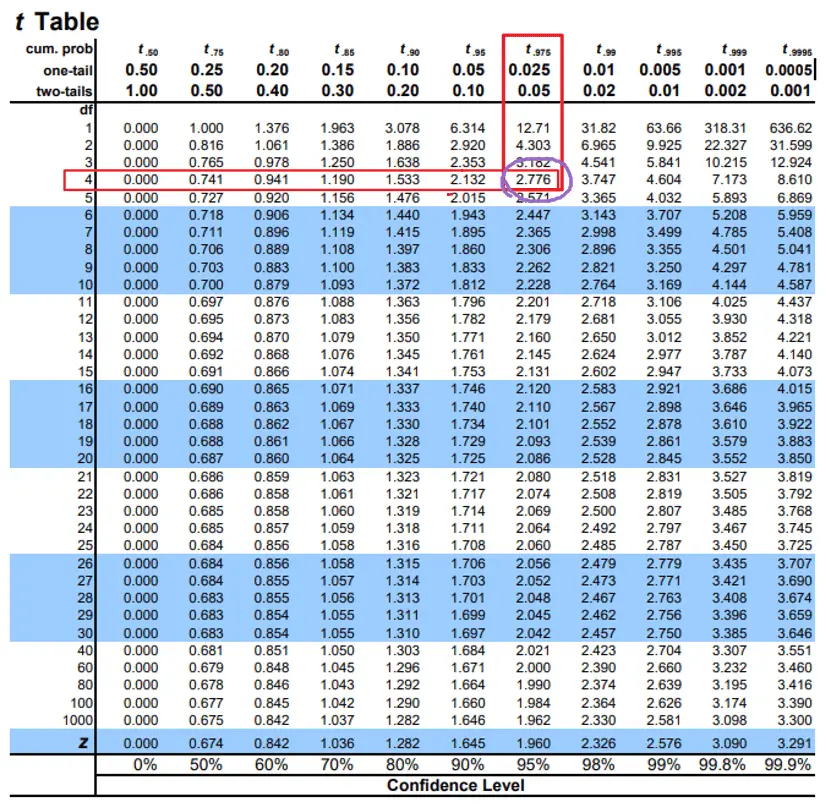
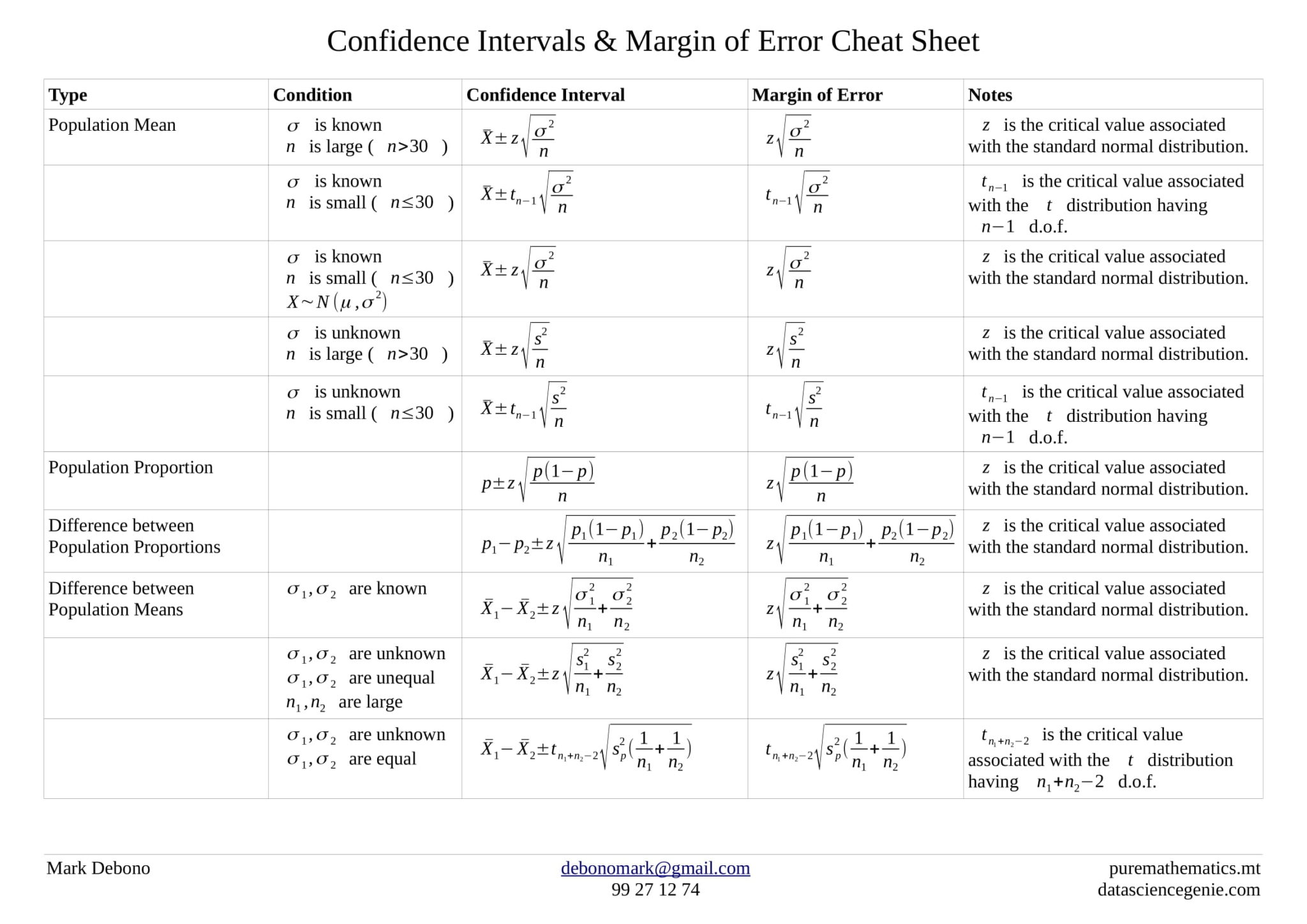
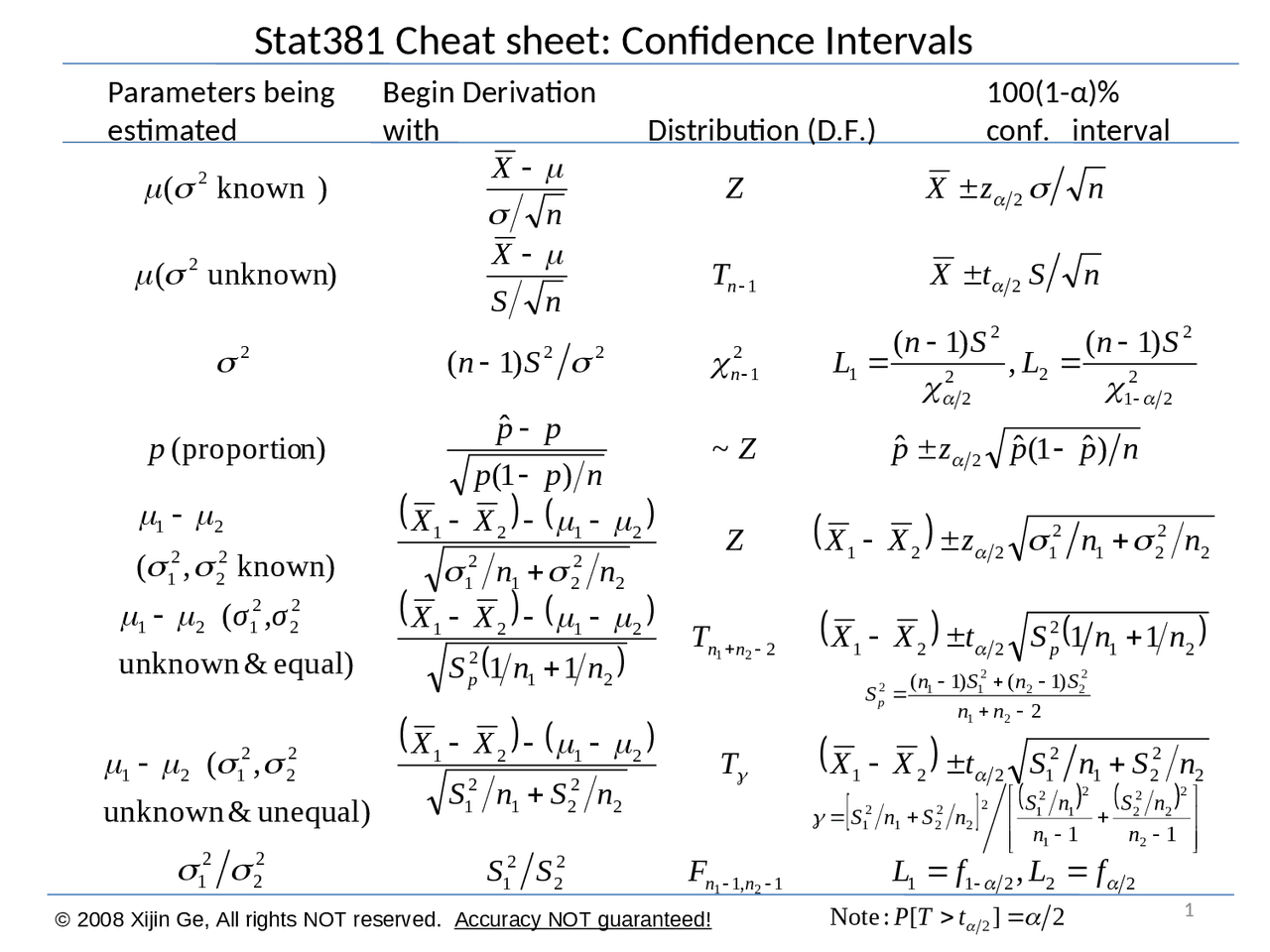
Confidence Interval Cheat Sheet
Confidence Interval Cheat Sheet - When do you use confidence intervals? B means a is less than b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. = 1 hypothesis test with.
Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. When do you use confidence intervals? 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. A > b means a is bigger than b. = 1 hypothesis test with.
= 1 hypothesis test with. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. When do you use confidence intervals? The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. A > b means a is bigger than b. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: B means a is less than b. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. Web confidence interval < < where with d.f.
How to Calculate Confidence Interval 6 Steps (with Pictures) Math
A > b means a is bigger than b. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat.
Confidence interval for two proportions calculator EmilieEmika
1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11. The reasoning of statistical estimation.
Introductory Statistics Confidence Estimation
Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. A > b means a is bigger than b. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. When do you use.
"AP Statistics Review CheatSheet The StatisticsMatrix at Redbubble
{ the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. B means a is less than b. The.
Confidence Interval Cheat Sheet
Web confidence interval < < where with d.f. Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: When do you use confidence intervals? = 1 hypothesis test with. 2 probability the chance of a certain event.
How To Compute A 95 Confidence Interval / 95 Confidence Interval Chart
{ the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A > b means a is bigger than b. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. A b means that a is less than or the same.
Confidence Interval in Statistics Formula and Mathematical
Web z interval t interval proportion interval 2 sample z interval symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 general • 2nd > vars • invnorm • stat > tests • 8: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. { the point that cuts.
Confidence Intervals Cheat Sheet puremathematics.mt
Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%. 1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = =.
Cheat Sheet Confidence Intervals Principles of Statistics I STAT
A b means that a is less than or the same as b. 2 probability the chance of a certain event happening. = 1 hypothesis test with. B means a is less than b. The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives:
2 Probability The Chance Of A Certain Event Happening.
A b means that a is less than or the same as b. A > b means a is bigger than b. B means a is less than b. Web confidence level = 1 − a so if you use an alpha value of p < 0.05 for statistical significance, then your confidence level would be 1 − 0.05 = 0.95, or 95%.
Web Z Interval T Interval Proportion Interval 2 Sample Z Interval Symbol 𝑧𝛼 2 𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 𝑧𝛼 2 General • 2Nd > Vars • Invnorm • Stat > Tests • 8:
The reasoning of statistical estimation margin of error and confidence level confidence intervals for a population mean how confidence intervals behave objectives: { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; When do you use confidence intervals? Web confidence interval < < where with d.f.
= 1 Hypothesis Test With.
1 d d d d de d e s et n n d t df n s n α µ µ −+ =− − = = − two sample variances 22 2 2 12 2 22 1 11 2 2 2 2 2 1 2 2 2 12 2 12 confidence interval for and 11.